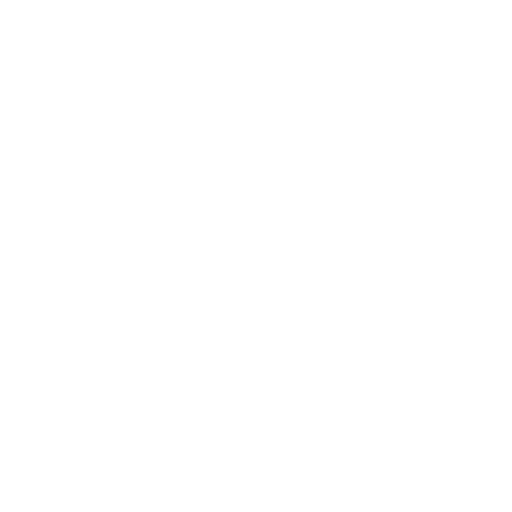
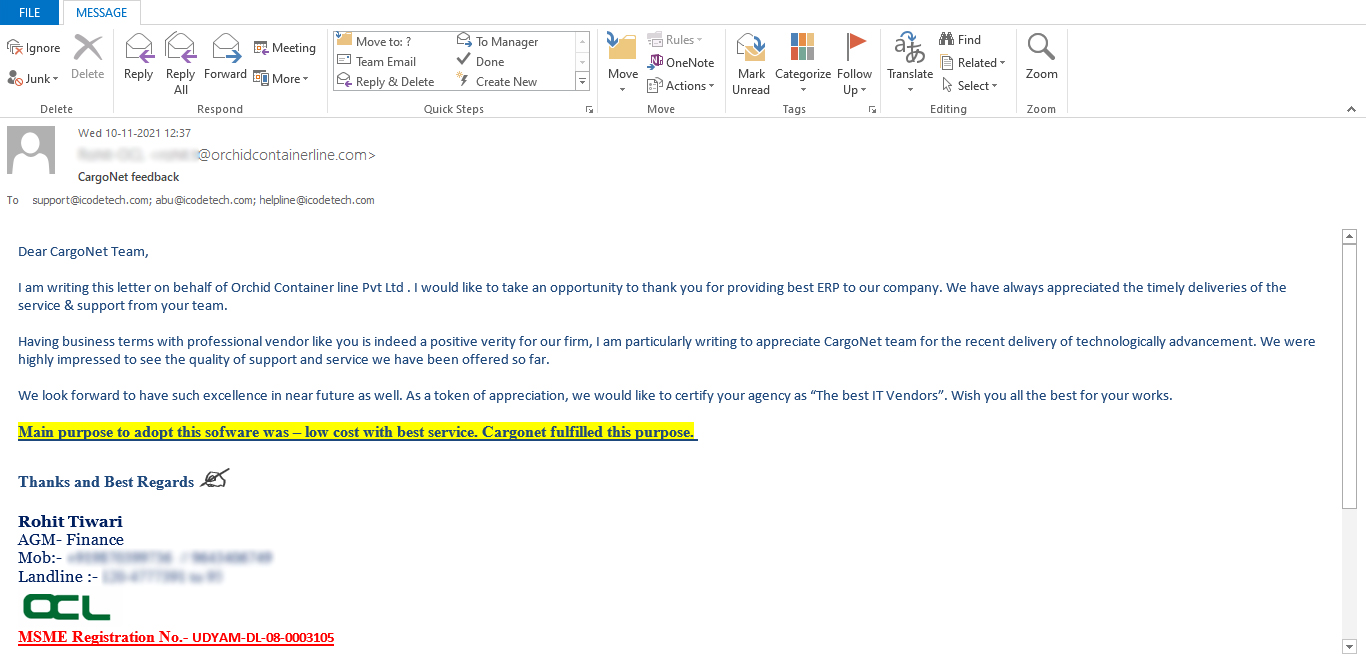
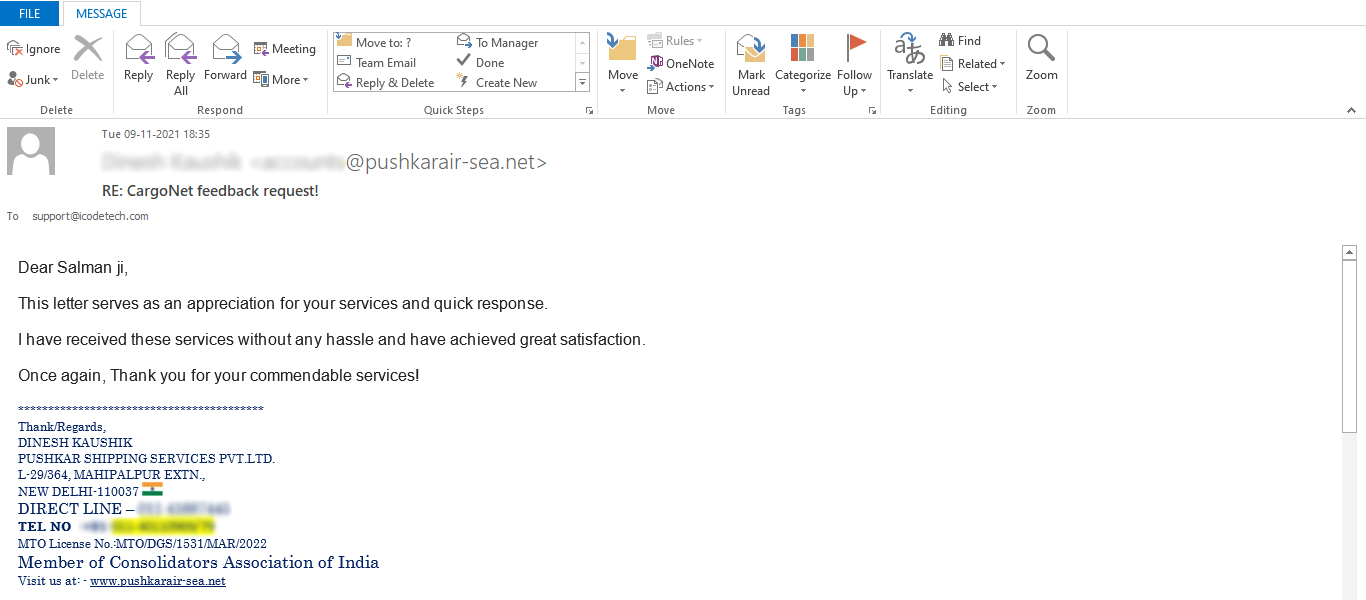
As the freight forwarding industry embraces digital transformation, cloud-based solutions are becoming essential tools for optimizing operations, enhancing efficiency, and elevating customer service. Amidst these advancements, ensuring robust data protection remains a top priority. In this blog post, we’ll discuss strategies that cloud-based freight forwarding software systems can employ to maintain client trust through enhanced data security measures.
Identifying the Challenges
Before diving into solutions, it’s vital to recognize the potential challenges associated with cloud-based platforms:As the freight forwarding industry embraces digital transformation, cloud-based solutions are becoming essential tools for optimizing operations, enhancing efficiency, and elevating customer service. Amidst these advancements, ensuring robust data protection remains a top priority. In this blog post, we’ll discuss strategies that cloud-based freight forwarding software systems can employ to maintain client trust through enhanced data security measures.
- Unauthorized Data Access: The risk of unauthorized individuals accessing sensitive information, leading to financial and reputational damage.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring adherence to industry regulations and data protection laws to avoid legal consequences.
- Data Integrity and Availability: Ensuring data remains intact and accessible, even in the face of unforeseen incidents.
Strategies for Enhancing Data Security
To address these challenges, freight forwarding software systems should implement a comprehensive approach to data security:
1. Encryption
- Data-at-Rest Encryption: By encrypting stored data, it becomes unreadable without the appropriate decryption key, providing an additional layer of security against unauthorized access.
- Data-in-Transit Encryption: Utilizing secure transmission protocols, such as SSL/TLS, ensures that data remains encrypted during transit between user devices and cloud servers.
2. Access Management
Robust access management is essential to controlling who can access sensitive data:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Defining user roles and assigning permissions based on job functions ensures that individuals only access the data necessary for their tasks.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Requiring multiple forms of verification adds an extra layer of security, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
3. Continuous Monitoring and Auditing
Continuous monitoring and periodic audits help detect and address security threats proactively:
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Monitoring network traffic enables the identification of suspicious activities and potential security breaches.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Analyzing security event data helps identify patterns and potential security incidents.
4. Data Backup and Recovery
Maintaining regular backups of data and testing recovery processes ensures business continuity in the event of data loss or corruption.
5. Compliance and Governance
Staying compliant with industry regulations and data protection laws is crucial:
- Regular Updates: Keeping software and security protocols up-to-date helps address emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
- Compliance Audits: Regular assessments ensure alignment with regulatory requirements and industry standards.
Conclusion
While the benefits of cloud-based freight forwarding systems are compelling, prioritizing data security is essential for safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining client trust. By adopting a multi-faceted approach that includes encryption, access management, continuous monitoring, data backup, and compliance adherence, freight forwarding businesses can operate confidently in a digital era. Investing in robust data security measures today can mitigate risks and protect against potential financial and reputational harm in the future.